-
Новости
- ИССЛЕДОВАТЬ
-
Страницы
-
Группы
-
Мероприятия
-
Статьи пользователей
-
Offers
-
Jobs
-
Форумы
The Foundational Power of Predictive Maintenance in Modern Industrial Asset Management
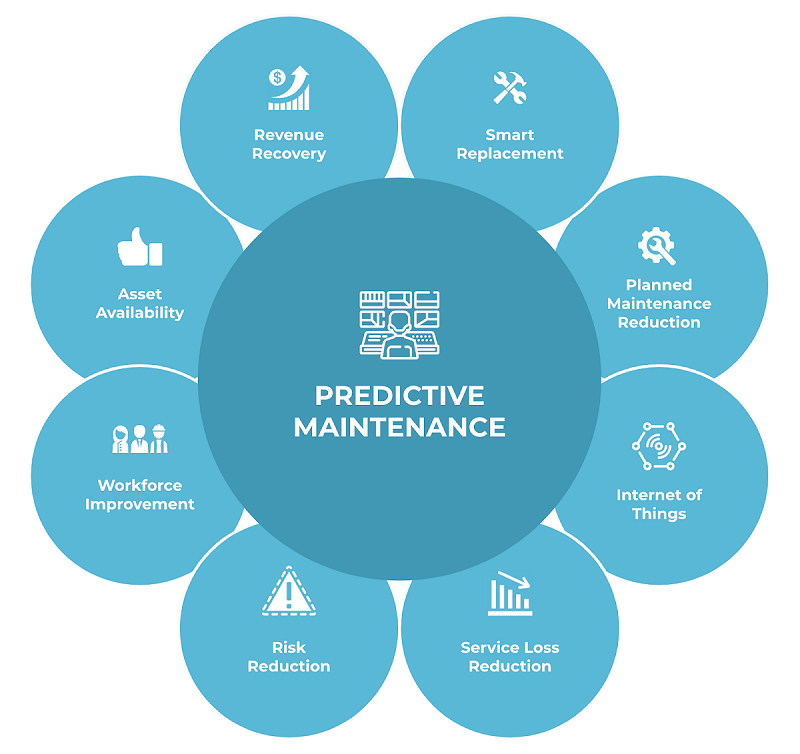
The evolution of industrial maintenance has reached a pivotal moment with the widespread adoption of Predictive Maintenance (PdM), a strategy that represents a profound leap beyond traditional reactive and preventive approaches. Instead of fixing equipment after it breaks (reactive) or performing maintenance on a fixed schedule (preventive), PdM uses data analysis tools to detect anomalies in operation and predict defects before they develop into failures. This proactive methodology allows organizations to perform maintenance only when it is truly needed, optimizing resource allocation and maximizing asset uptime. The immense value unlocked by this approach is driving one of the fastest-growing sectors in the industrial technology space. The global Predictive Maintenance Market Is Projected To Grow from USD 43.88 Billion to 449.6 Billion by 2035, Reaching at a CAGR of 26.2% During Forecast 2025 - 2035. This staggering growth underscores a fundamental shift towards data-driven, intelligent asset management across all industries.
At the heart of any predictive maintenance program are the technologies that capture the real-time health and performance data of industrial assets. This is primarily enabled by the Internet of Things (IoT). A vast array of sensors are deployed on critical machinery to continuously monitor key operational parameters. Vibration sensors can detect subtle changes in the resonant frequency of a motor, often an early sign of bearing wear. Thermal imaging cameras can identify hotspots in electrical panels that indicate a failing connection. Acoustic sensors can listen for abnormal sounds that signify stress or misalignment in mechanical components. This raw data is then collected through industrial gateways and transmitted to a central system for analysis. The falling cost and increasing sophistication of these IoT sensors have been a primary catalyst, making it economically viable to instrument a wide range of equipment, from massive turbines to smaller, yet critical, pumps and motors.
However, collecting vast amounts of sensor data is only the first step. The true intelligence of predictive maintenance lies in the ability to analyze this data to find meaningful patterns and make accurate forecasts. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play a transformative role. Machine learning algorithms are trained on historical data, which includes both normal operational data and data leading up to past failures. By analyzing this history, the AI model learns to recognize the complex, multi-variate signatures that precede a fault. When new, real-time data is fed into the model, it can accurately assess the equipment's health, calculate its remaining useful life (RUL), and issue a predictive alert days, weeks, or even months before a failure is likely to occur. This predictive power is what distinguishes PdM from simpler condition-based monitoring.
The benefits of implementing a robust predictive maintenance strategy are profound and far-reaching. The most significant advantage is the drastic reduction in unplanned downtime, which is a major source of lost revenue for industrial operations. By scheduling maintenance proactively, companies can avoid catastrophic failures and conduct repairs during planned shutdowns, maximizing productivity. This leads to significant cost savings, not only from avoiding downtime but also from optimizing maintenance schedules and extending the life of components. Furthermore, it enhances worker safety by identifying potentially dangerous equipment conditions before they result in an accident. As a cornerstone of Industry 4.0, predictive maintenance is transforming factories into smart, self-aware environments, paving the way for a future of autonomous and highly resilient industrial operations.
Explore More Like This in Our Regional Reports:
China Security Software Telecom Market Size
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
