Power System Simulator Market Size, Demands, Growth, Forecast & Segments 2032 | UnivDatos
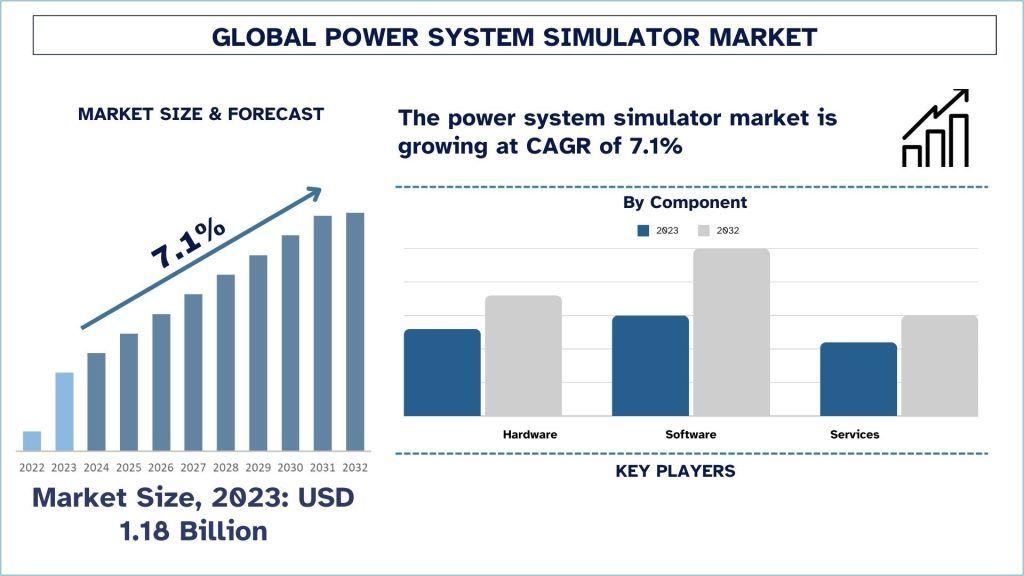
The Power System Simulator Market was valued at approximately USD 1.18 Billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a robust CAGR of around 7.1 % during the forecast period (2024-2032)
As North America experiences significant economic growth and population expansion, the electricity demand continues to rise. This growing demand challenges the existing power infrastructure, necessitating technological advancements, system management, and regulatory frameworks. This article explores the factors driving electricity demand in North America, the systems employed to maintain a reliable power supply, and the government regulations that support these efforts.
Growing Electricity Demand
Economic Growth and Urbanization
North American energy growth and urbanization also play a significant role in the growing electricity demand. As industries expanded and cities grew, the requirements for energy-intensive activities—privileged ones in the manufacturing industry, those of transportation, or just plain commercial services—started to skyrocket. Urbanization also drives up residential electricity consumption as more people move into cities and use modern home appliances and consumer electronics.
Technological Advancements
Electricity demand is increasing due to technological advancements. The growing number of electric vehicles (EVs, smart home gadgets, and data centers are consuming a significant amount of energy. For example, the rising number of EVs needing to be charged is putting more load on the power grid. When a consumer plugs an EV into a 220-volt charging station, it adds nearly as much demand for electricity as another house would.
Climate Change and Electrification
The push to electrify many sectors to fight climate change is ramping up electricity demand. While the policies that encourage switching from natural gas and oil to electric heating systems, approve of transitioning away from gasoline/diesel public transportation towards ELECTRIC public transport options, or those that support the replacement of fossil fuel power generations with renewables are essential to decrease carbon emissions, it also means BIGGER consumption of electricity.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/reports/power-system-simulator-market?popup=report-enquiry
Electricity Supply Components
Smart Grids Overview Smart Grids are designed with digital technology to facilitate monitoring and managing the flow of electricity from generation points through distribution lines at each household Point. Eligible resources are necessary to help address the increasing need for electricity while also contributing toward greater reliability and efficiency on the grid.
Features and Benefits
Real-Time Monitoring: In the case of power supply and demand, smart grids enable real-time monitoring that can correlate to fluctuations or potential problems faster than traditional methods.
Demand Response: These systems enable demand response programs by which consumers can modify their consumption during peak periods to stabilize the grid.
Integrating Renewables: Smart grids are a must-have for integrating renewable sources of energy such as solar, wind, etc., which by nature have variable output factories.
Energy Storage Systems Overview
With the rising penetration of varying distributed energy resources (DER), Energy Storage Systems (ESS) have become a key enabler for grid stability and reliability. Whether its excess electricity generated from late evening to early morning hours is stored and used in these peak periods or housed in a separate ESS discharge power reserve for the car.
Types and Applications
Short-term Energy Storage (Battery): Lithium-ion batteries are the most common battery storage technology designed to rapidly respond to supply and demand.
Pumped Hydro Storage: Use extra electricity or evacuate the differential demand through pumping and lodge a body of water in a height sphere. This holds the water and, when needed, releases it to create electricity during periods of high demand.
Stationary energy storage: Electrical stationary systems use the principle of electrical resistance to store excess heat or cold for later to improve electricity supply and demand settlements.
Click here to view the Report Description & TOC: https://univdatos.com/reports/power-system-simulator-market
Distributed Energy Resources Overview
DER stands for distributed energy resources, which are small-scale power generators or storage systems used on the distribution side of an electrical service point. They are a key resource to improve grid reliability and satisfy local energy needs.
Types and Benefits
Solar Photovoltaics (PV): These systems generate electricity from sunlight, which reduces reliance on power plants located far away and has the potential to provide grid stability.
Wind Turbines: Small wind turbines generate electricity from the power of the wind, providing a renewable source of electrical energy available to local communities.
Microgrids: The localized grids that can operate independently or connect to a main grid to provide backup resources.
Automated Metering Infrastructure Overview
Smart meters and associated communication networks that give detailed insights into electricity usage patterns fall under advanced metering infrastructure (AMI). The power system simulator makes grid management and demand response more effective.
Features and Benefits
Precision In Billing: Since smart meters remain connected and provide real-time data of electricity consumed, it results in accurate billing.
Outage Management: The power system simulator can quickly detect and pinpoint the location of power outages, leading to faster restoration times and better service reliability.
Save Energy: Homeowners can learn about their home's electricity consumption to save energy and money.
Government Regulations
United States FERC: Federal Energy Regulatory Commission and The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) oversees interstate electricity transmission and has the statutory authority to issue regulations ensuring efficient and fair wholesale power markets.
Clean Power Plan The widely known Clean Power Plan from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is intended to reduce carbon emissions created by power plants. It promotes cleaner energy and improved efficiency, which has a ripple effect on electricity demand and supply.
State-Level Initiatives To varying degrees, individual states have adopted rules and incentives to encourage renewable energy development alongside policies that promote greater efficiency in the electricity industry. For instance, California's Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) will require the state to obtain much of its electricity from renewable sources.
Canada
National Energy Board (NEB)
The National Energy Board (NEB) regulates Canada's interprovincial and international aspects of electricity. NEB ensures the reliability and sustainability of the country's energy infrastructure.
Pan-Canadian Framework on Clean Growth and Climate Change
Canada's Pan-Canadian Framework on Clean Growth and Climate Change outlines measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote clean energy. The framework includes initiatives to increase the use of renewable energy and improve energy efficiency.
Provincial Programs
Provinces such as Ontario and British Columbia have implemented renewable energy targets and efficiency programs. These initiatives support the transition to a low-carbon economy and help meet growing electricity demand.
Conclusion
The electricity demand will be supported by the increasing demands of economic growth in North America, which is followed by technological development and the desire to combat climate change. Several systems, such as smart grids, energy storage, distributed energy resources, and advanced metering infrastructure, are being adopted to meet this requirement. These efforts are strongly supported by government regulations and policies at federal, state, and provincial levels to enhance a secure electricity supply further. With the energy landscape constantly changing, meeting growing electricity demand will require collaboration between utilities, regulators, and consumers. By embracing new technologies and policy solutions, North America can forge a resilient, clean energy future. According to the UnivDatos growing awareness of cybersecurity threats also prompts the use of simulators for vulnerability assessment and defense strategy development. Supportive government policies and regulations promoting renewable energy adoption and grid reliability significantly boost the market, as utilities aim to comply with these mandates through advanced simulation tools.
Contact Us:
UnivDatos
Email: contact@univdatos.com
Contact no: +1 978 7330253
Website: www.univdatos.com
Linked In: https://www.linkedin.com/company/univ-datos/
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
